Converting Customary Units of Measurement
We have been working on converting Customary Units of measurement in Math. In problems which involve measurements such as width, length, height, weight, capacity or temperature, it is often necessary to convert from one measurement unit to another.

Basic Conversion Rule:
To convert from a LARGER unit to a SMALLER unit...MULTIPLY
To convert from a SMALLER unit to a LARGER unit...DIVIDE
We have four different strategies that we have learned to help us with conversions.
1. Draw a picture.
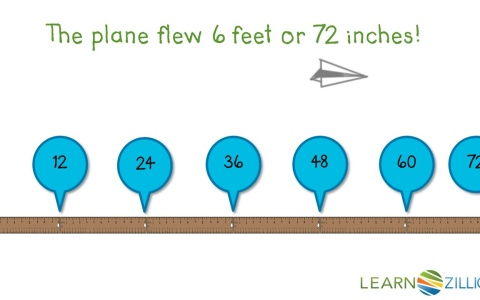
2. Make a t-chart.
3. Use the saying.


4. Use a proportion.

Here are a couple of videos that further explain conversions in the customary system:
Here are some games that will help solidify this skill:
Please let me know if you have any questions!